How to Set Up Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code is a powerful, extensible, and lightweight code editor that has become one of the preferred code editors in the Python community.
In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to install Visual Studio Code and set it up for Python development, as well as how to become more productive with VS Code.
Let’s dive in!
Installing Visual Studio Code
This section will cover how to install VS Code on macOS step by step. Let’s get started.
NOTE
Due to the essential differences between Windows and macOS, Windows users need to do minor modifications to install VS Code. However, installing VS Code on Windows is straightforward and similar to installing other Windows applications.
Steps to Install Visual Studio Code
Download Visual Studio Code First, download Visual Studio Code for macOS or Windows from its official website. The download page detects your operating system automatically and displays a big button for downloading the latest version of the Python installer on your computer. If it doesn’t, click the arrow-down button and choose the stable VS Code release that matches the operating system installed on your computer:
Extract the Archived Contents Double-click the downloaded file to extract the archived contents:
Move the Application to the Applications Folder Move the Visual Studio Code application to the Applications folder to make it available in the macOS launchpad:

Launch Visual Studio Code Launch Visual Studio Code, and then open a folder where your Python scripts exist or create a new one. For example, create a new folder on your Desktop and name it
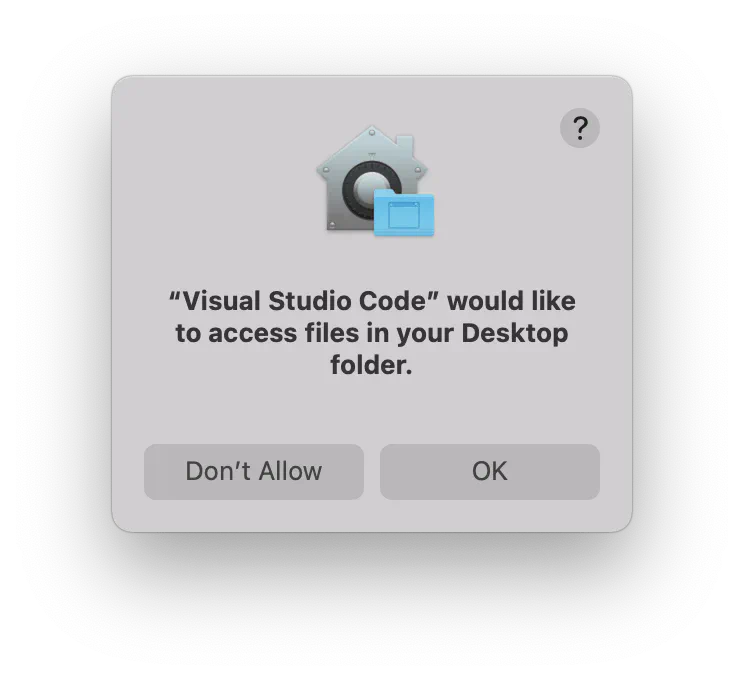
py_scripts. Then try to open the folder in VS Code.Usually, VS Code needs your permission to access files in your Desktop folder. Click OK:
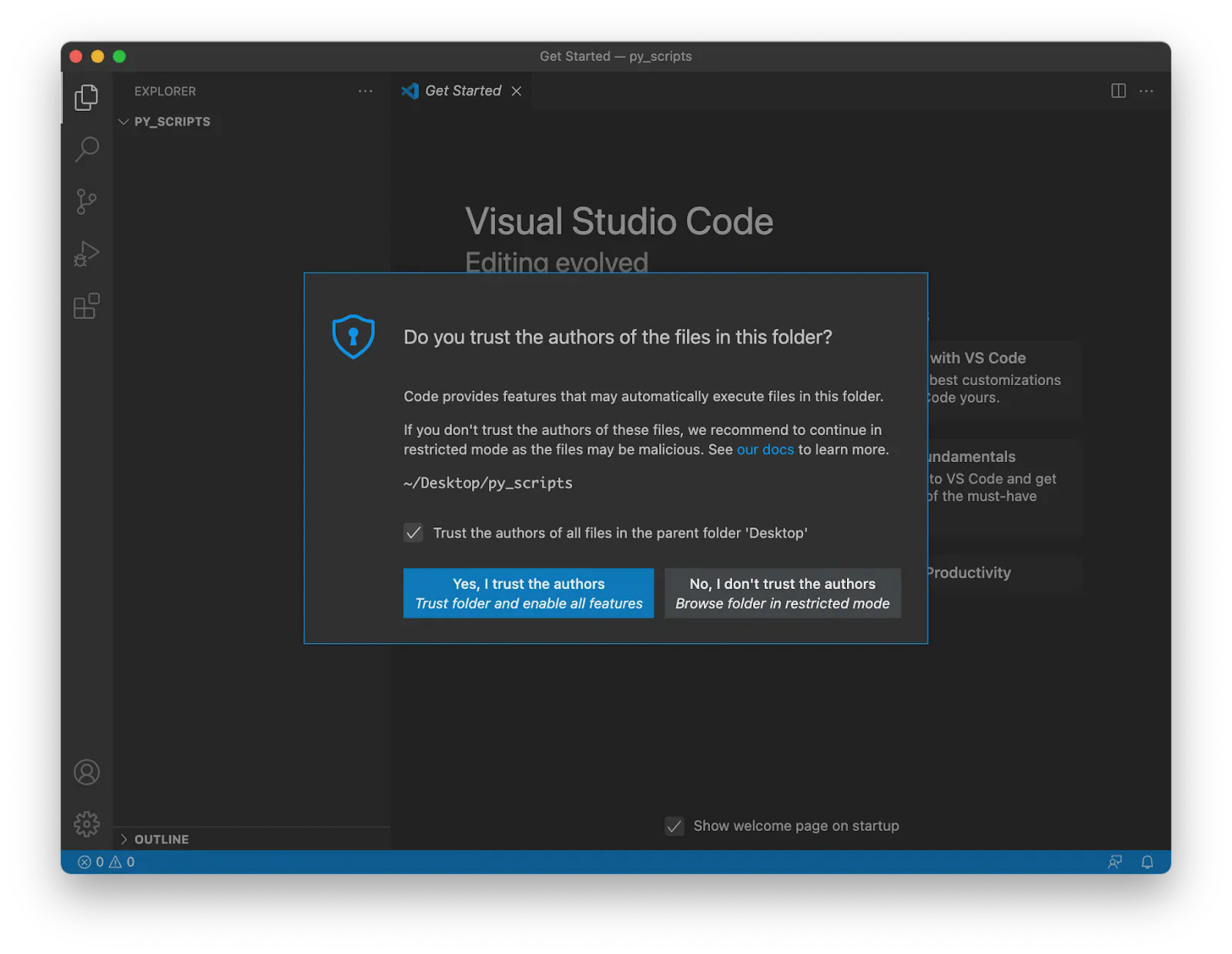
You may also need to declare that you trust the authors of the files stored in your Desktop folder:
Create a New File Create a new file with a
.pyextension. For example, create a new file and name itprog_01.py. VS Code detects the.pyextension and suggests installing a Python extension: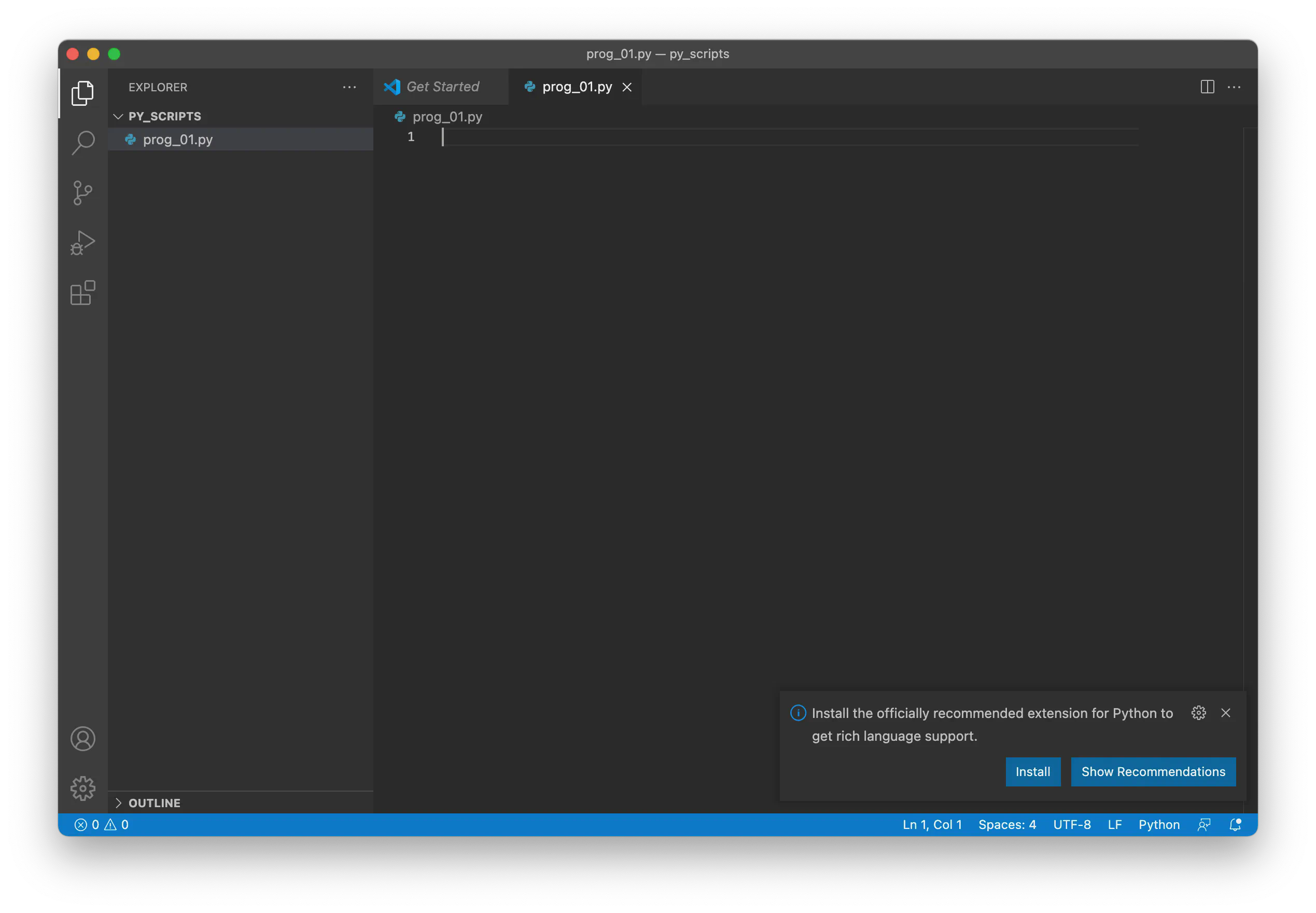
To work with Python inside VS Code, we need to use the Python extension, which brings many useful features, such as code completion with IntelliSense, debugging, unit testing support, and more:
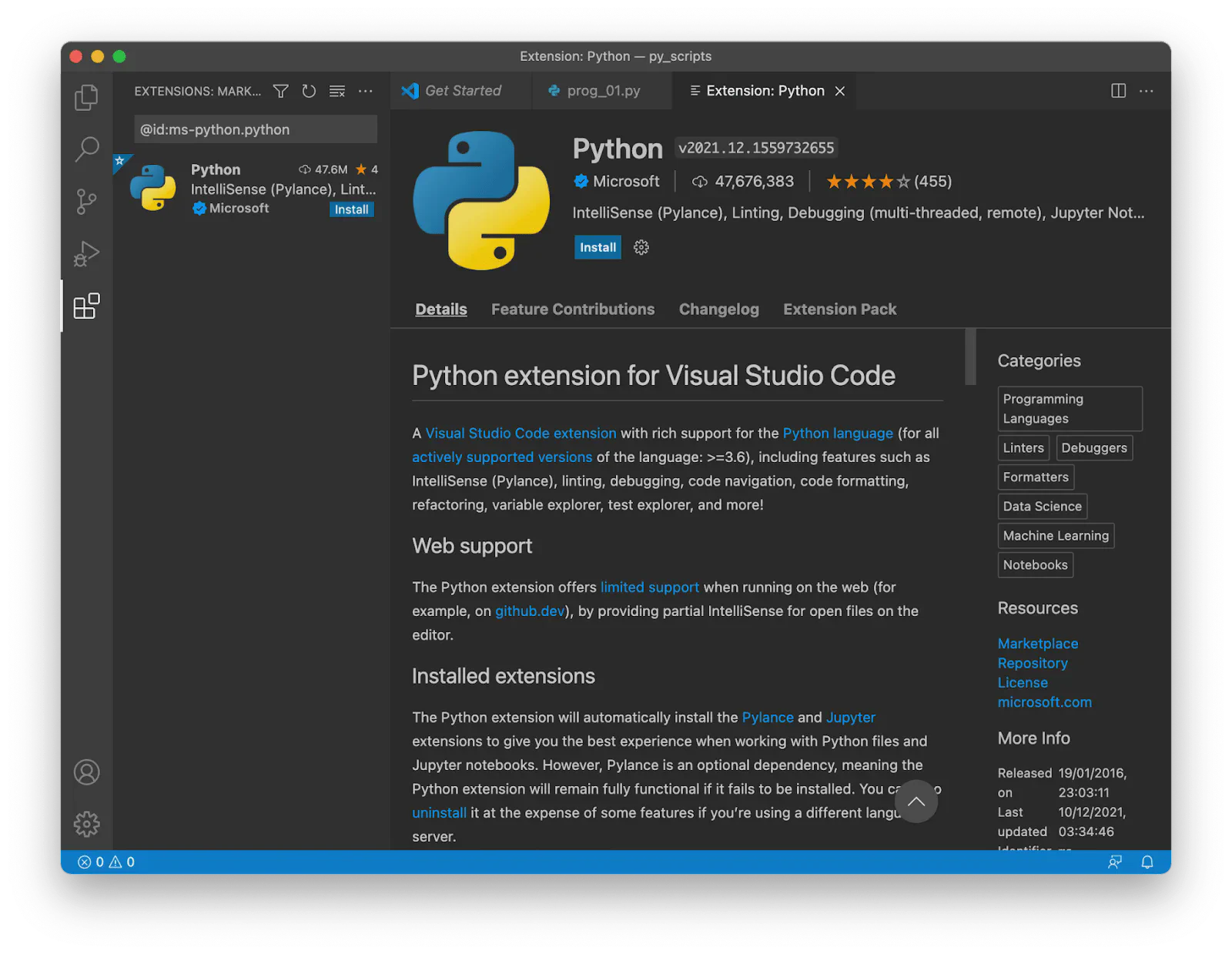
Install the Python Extension Click Install to install the Python extension:
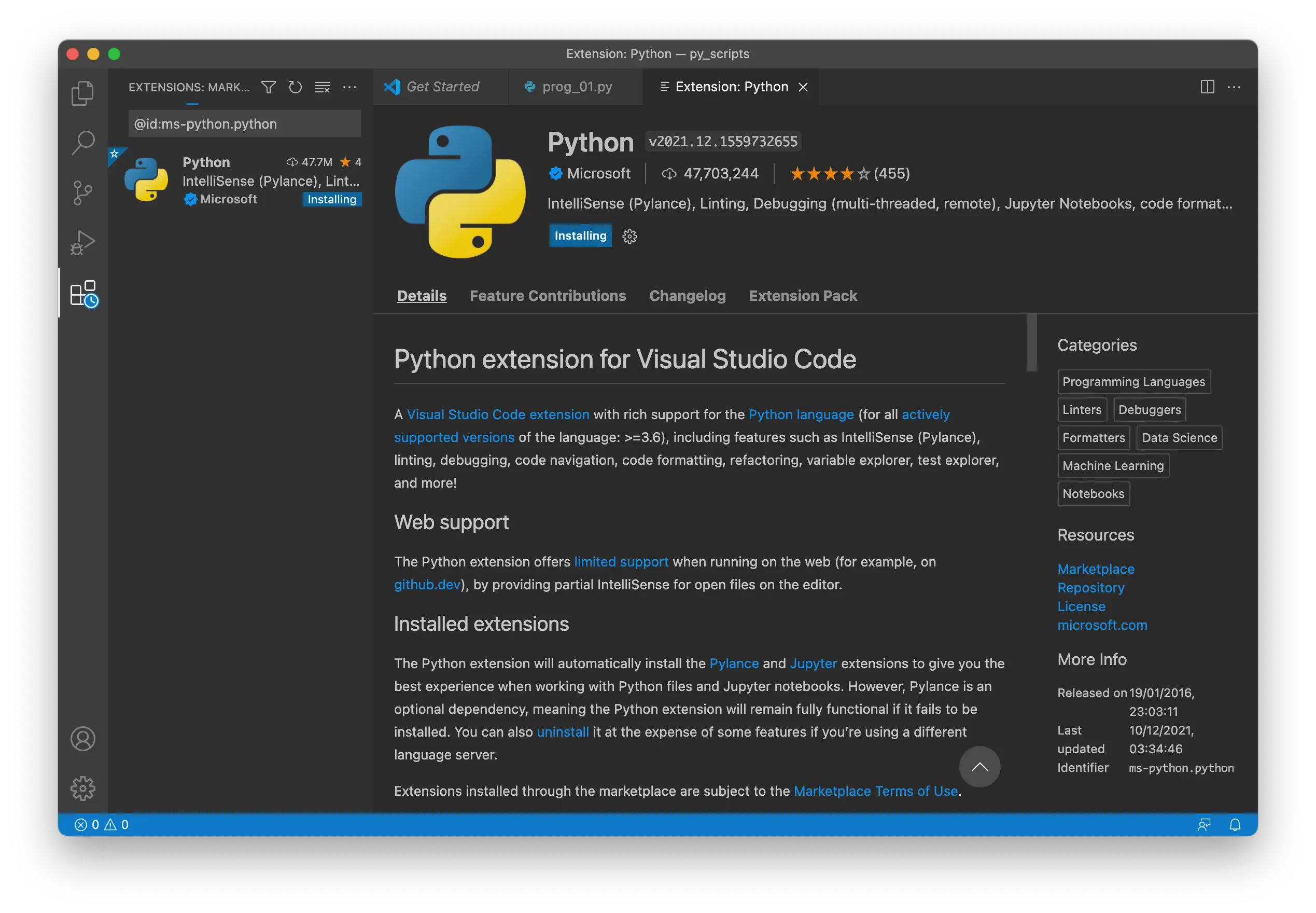
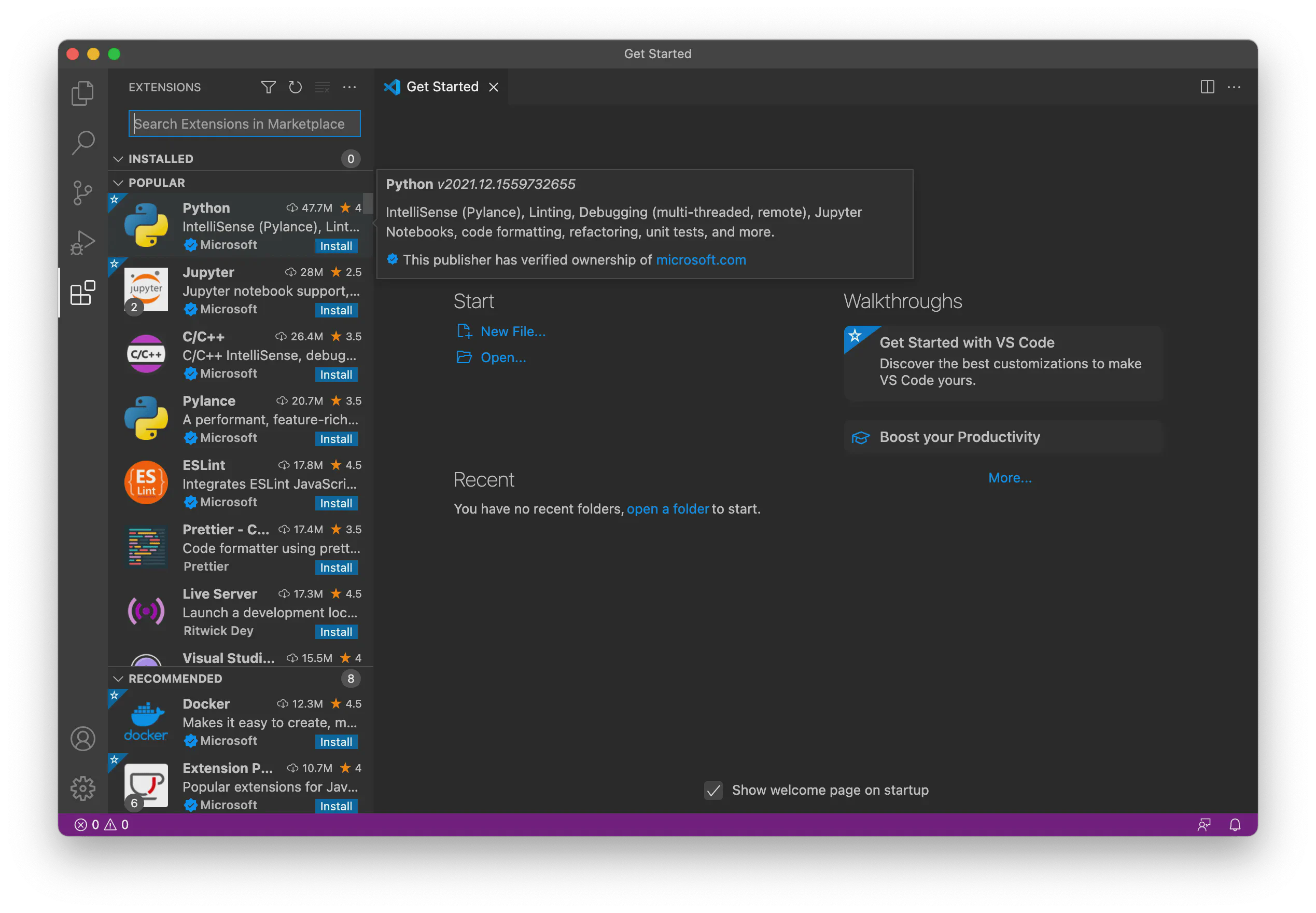
Browse Extensions if Needed You can also install the Python extension by browsing extensions. Click the Extensions icon on the left side of VS Code:

This will show you a list of the most popular VS Code extensions on the VS Code Marketplace. Select the Python extension and install it:
Select a Python Interpreter Once the extension is installed, you have to select a Python interpreter. Click Select Python Interpreter:
Then select the recommended Python interpreter on the list:
If you have multiple Python versions installed on your Mac, choose the latest version:
You can also select a Python interpreter using the Python: Select Interpreter command from the Command Palette. To do so, press
CMD + SHIFT + P, type “Python,” and choose Select Interpreter.
Creating and Running a Python File in VS Code
Now that we have everything set up, let’s write and run Python code inside VS Code.
Example Code
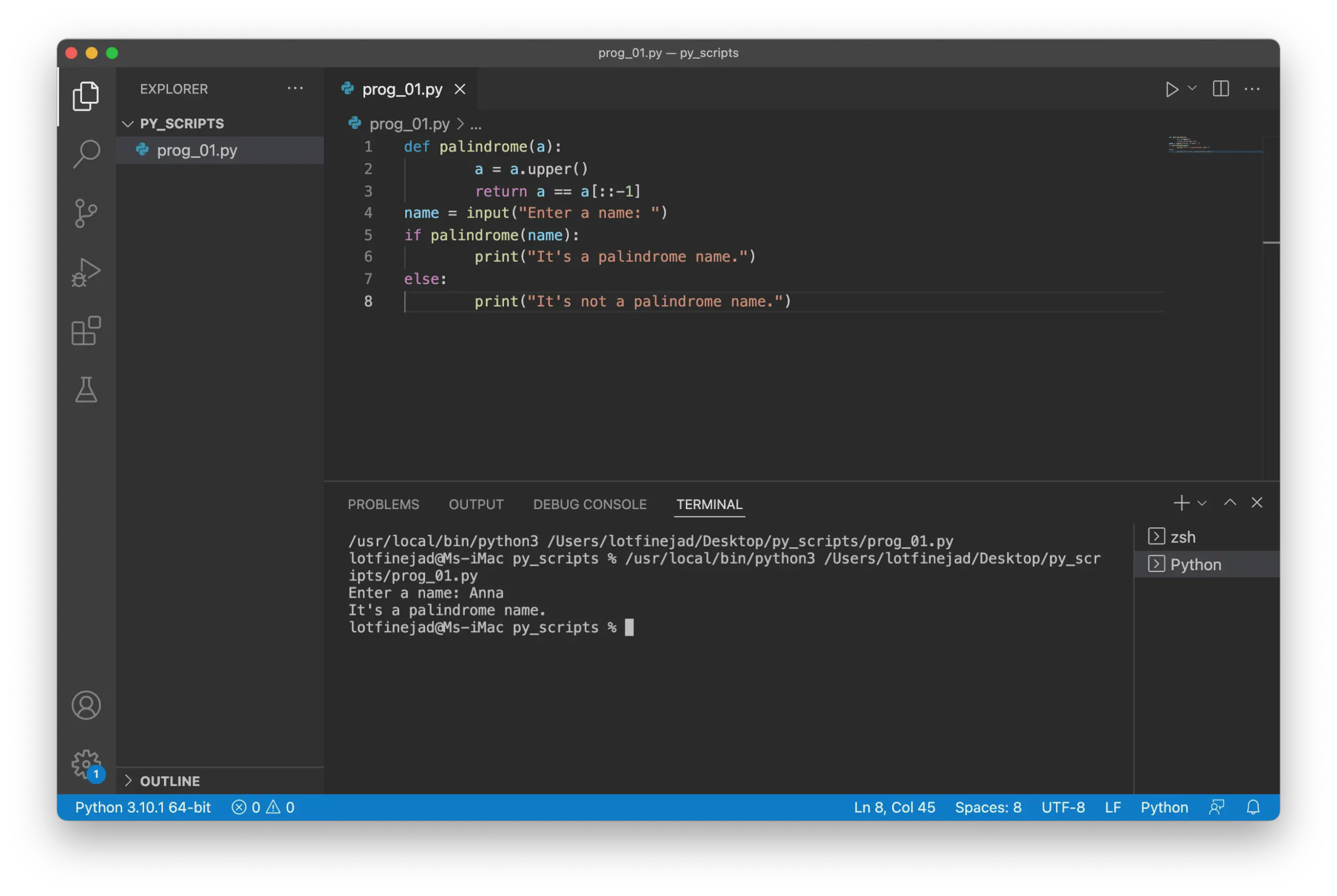
Write the following code in VS Code:
def palindrome(a):
a = a.upper()
return a == a[::-1]
name = input("Enter a name: ")
if palindrome(name):
print("It's a palindrome name.")
else:
print("It's not a palindrome name.")Run the Code
Run the code by clicking the ▶️ button in the top-right corner of VS Code.
- First, it asks for a name in the integrated terminal. Enter a name and press Return.
- If the entered name is a palindrome (e.g., Hannah, Anna, or Bob), the output will be:
It's a palindrome name. - Otherwise, it will output:
It's not a palindrome name.
Using the Integrated Terminal
As you’ve seen, all outputs from the program appear in the integrated terminal. Let’s explore this feature further.
Visual Studio Code brings great convenience by embedding this feature into the IDE because executing terminal commands is an essential part of writing code.
How to Access the Terminal
- Open the terminal using the shortcut:
- Hold down the Ctrl key.
- Press the backtick key once.
- The terminal should appear at the bottom of your VS Code window.
- Or navigate to the View > Terminal menu option.
Terminal Features
- Kill the Terminal: Click the bin icon in the top-right of the terminal window.
- The integrated terminal uses your system’s installed shells, such as:
- PowerShell or Command Prompt on Windows.
- Bash or Zsh on macOS and Linux.
Customizing the Terminal
Open the terminal settings page.
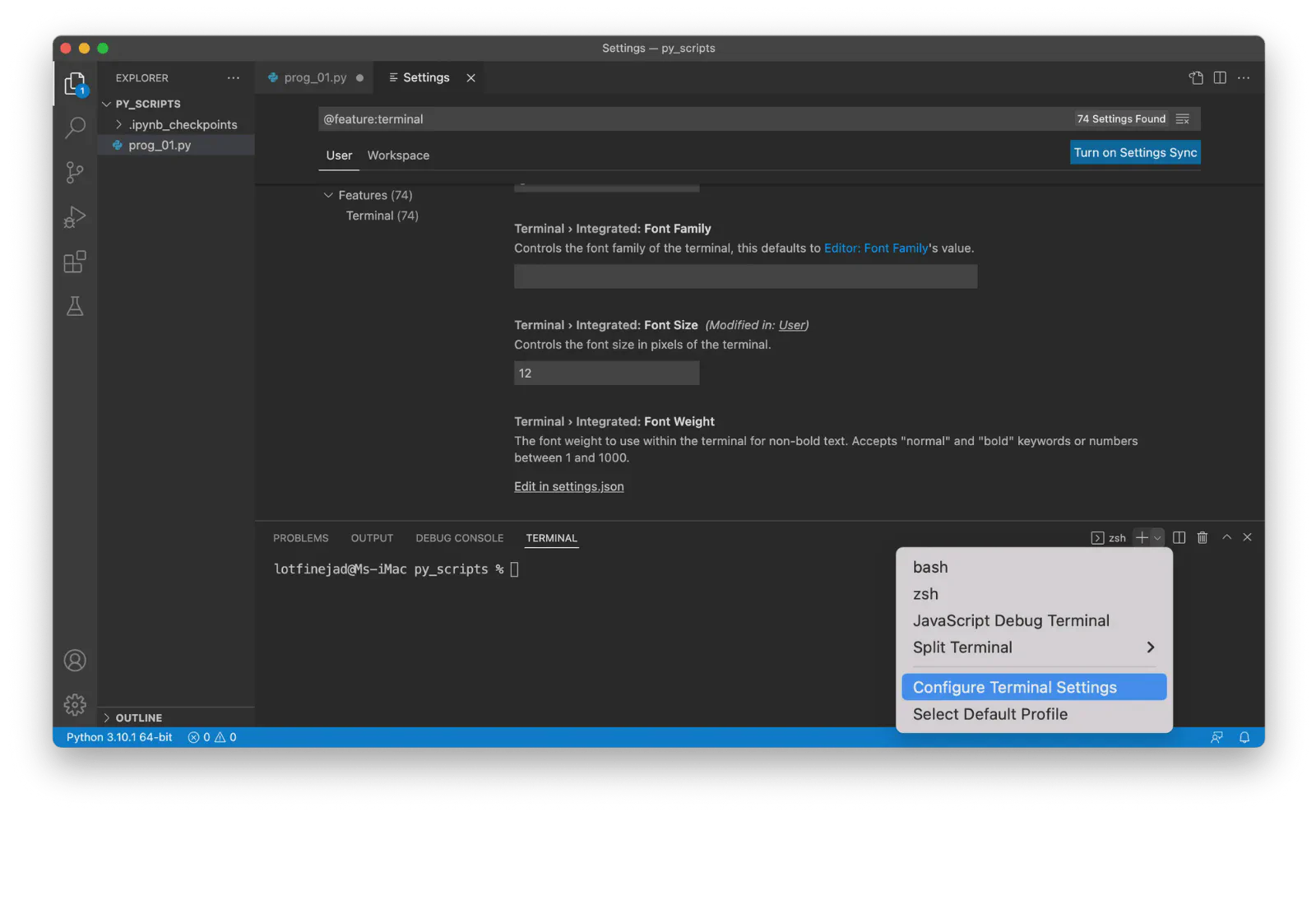
Click the arrow-down button in the top-right corner of the terminal window.
Select Configure Terminal Settings to customize font, spacing, and cursor style:
Switching Between Shells
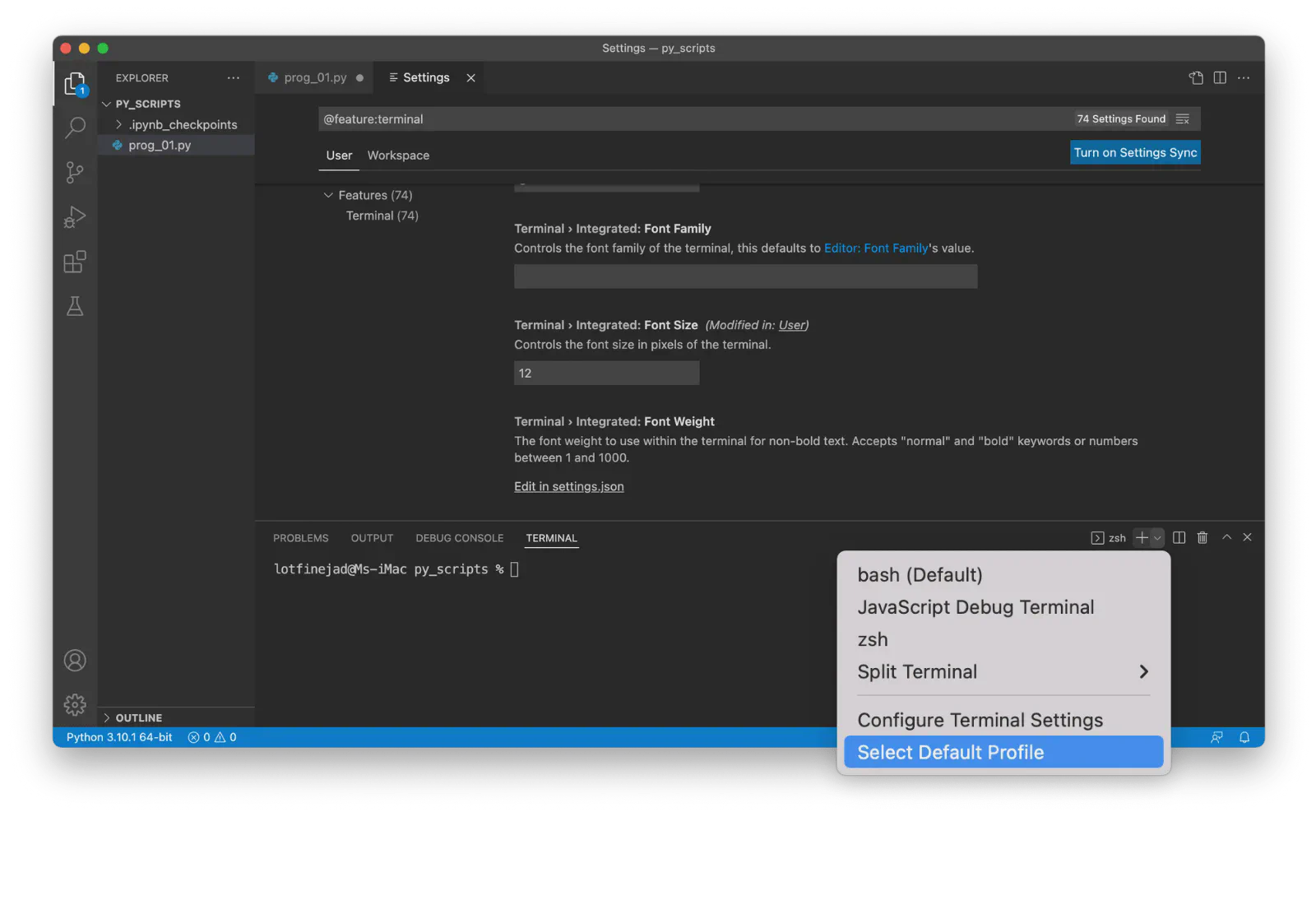
Click the arrow-down button in the terminal window.
Select the Select Default Profile option:
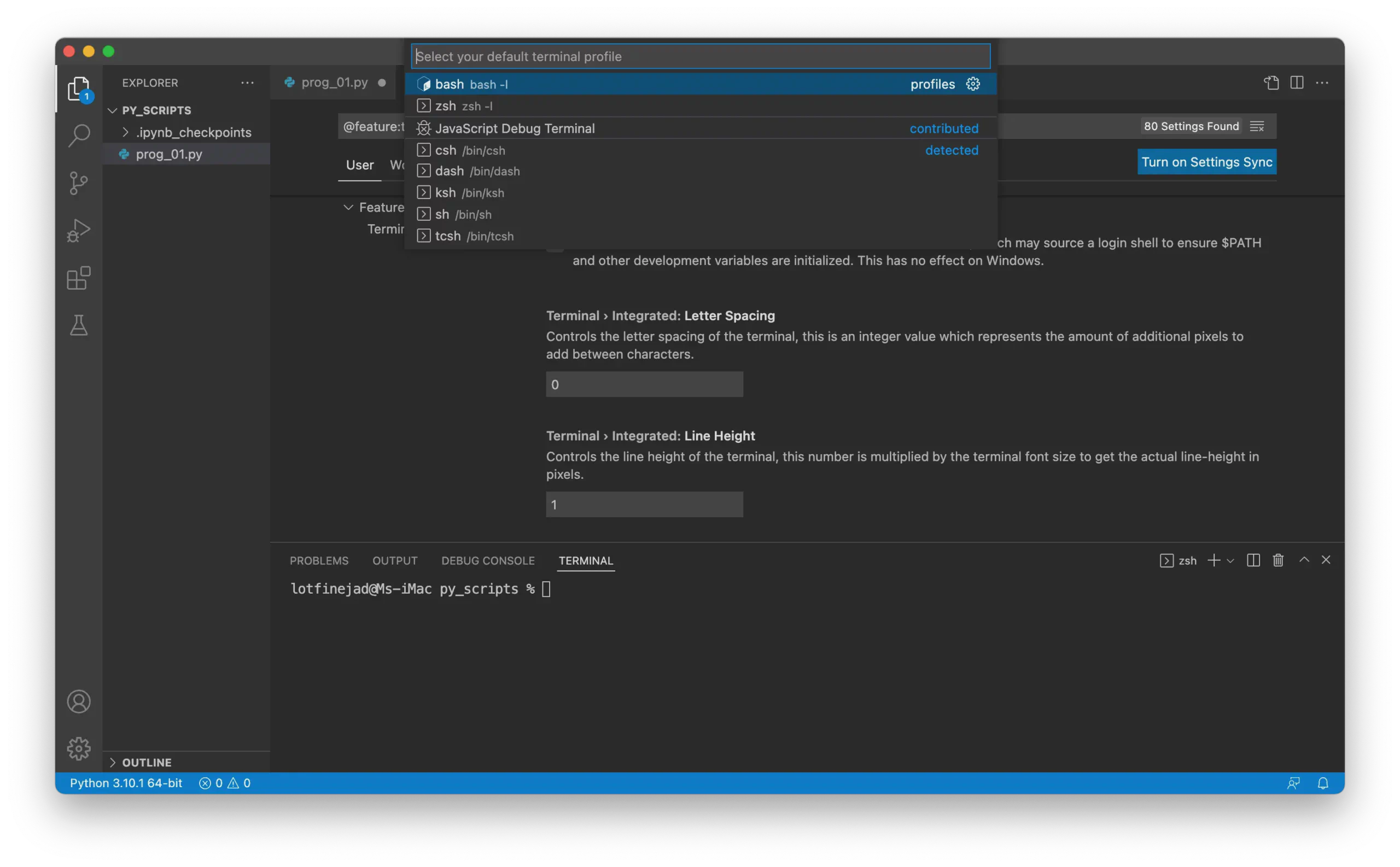
A pre-populated list of available shells will appear. Select your preferred default shell, such as Bash:
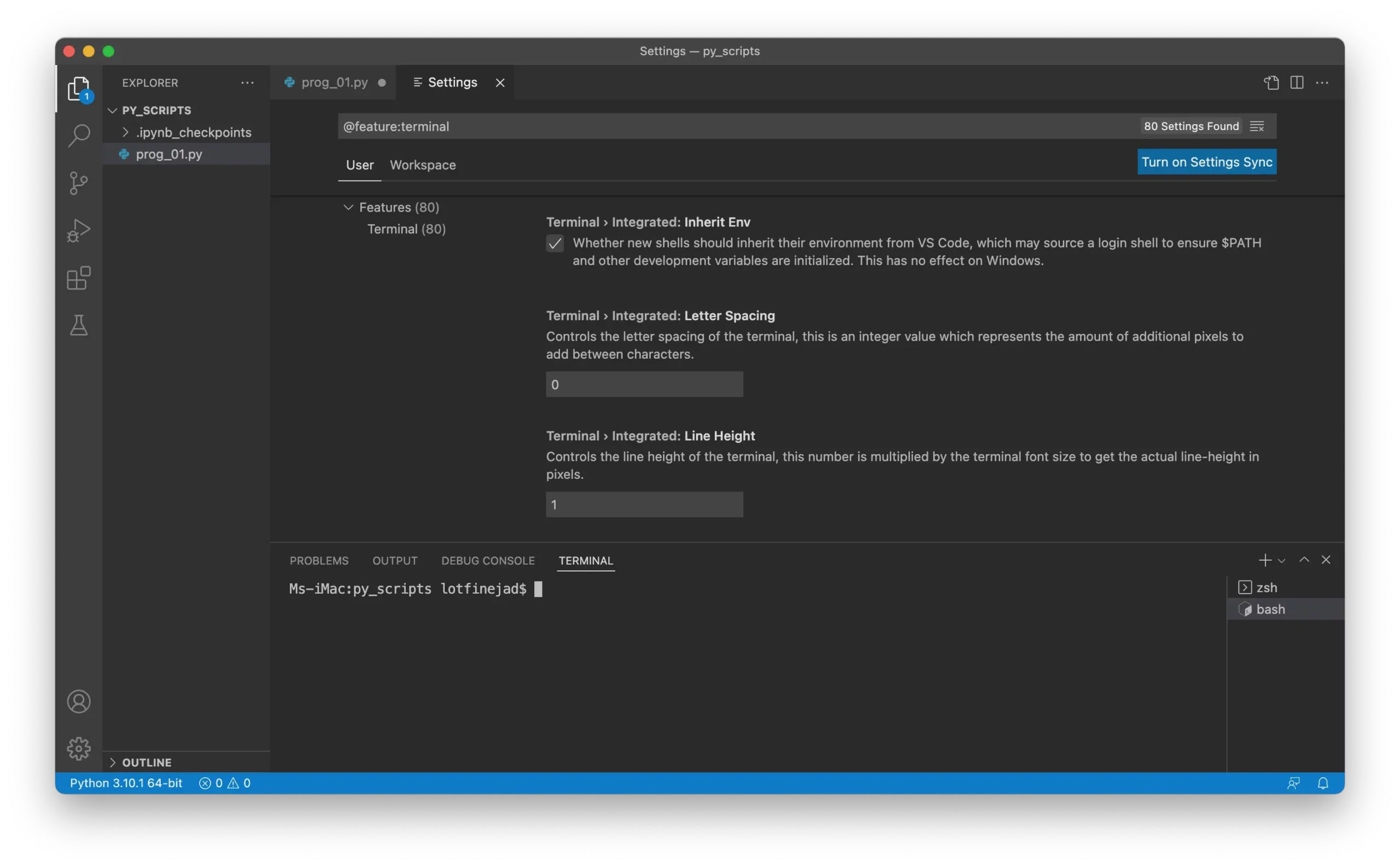
Once you create a new terminal (by clicking the plus icon in the terminal window), it will open using the selected shell:
Using the REPL
Another useful feature of VS Code is running single or multiple lines of Python code using the REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop).
How to Use REPL
Write the following statement in your Python file:
print("Hello, world!")Select the statement, right-click, and choose Run Selection/Line in Python Terminal:
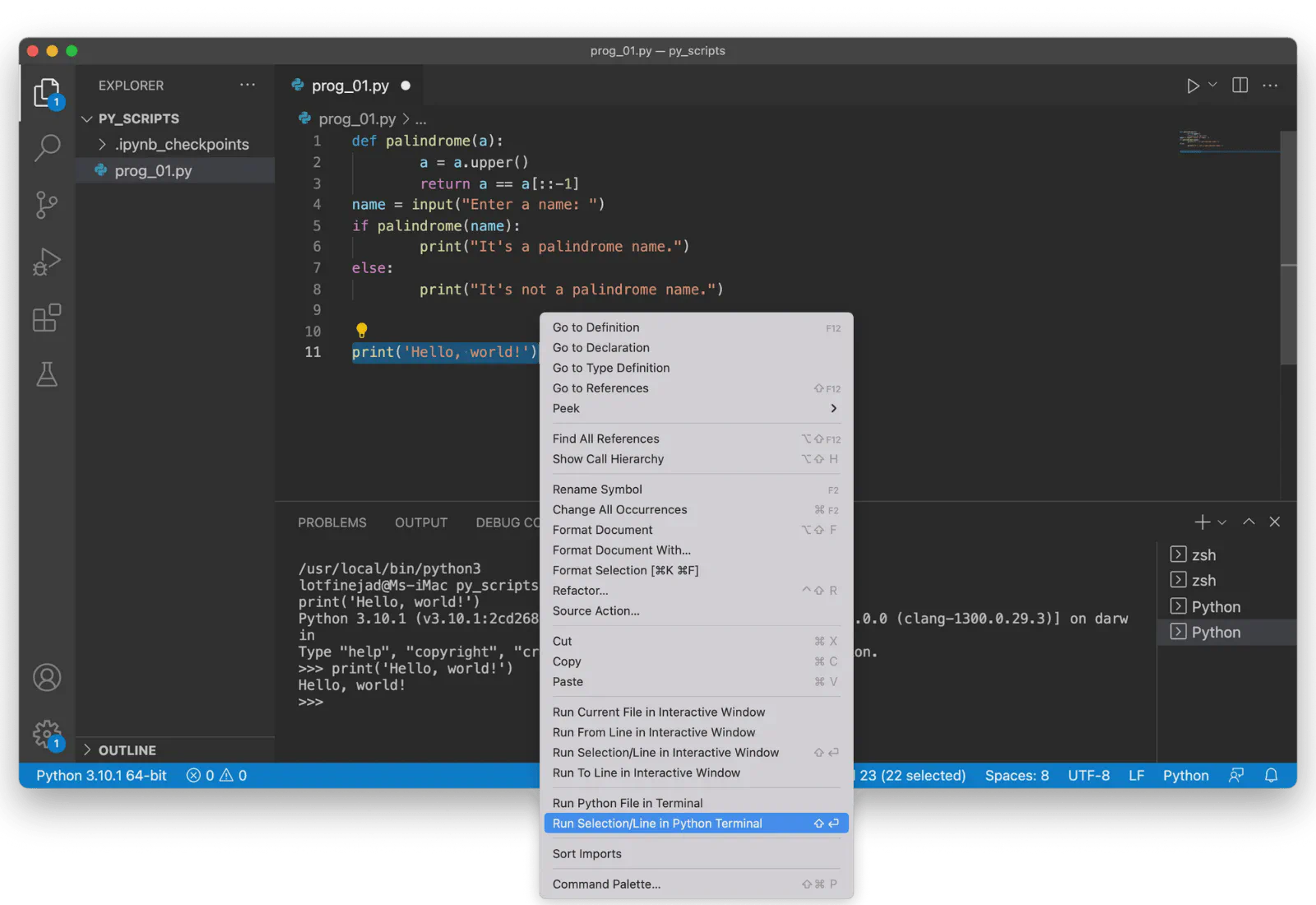
Output in REPL
The output will appear in the integrated terminal, but in a special format known as REPL.
What is REPL?
- REPL stands for Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop.
- It provides an interactive way to run commands within the terminal.
- The three arrows (
>>>) indicate an input line in REPL.
Starting REPL Directly
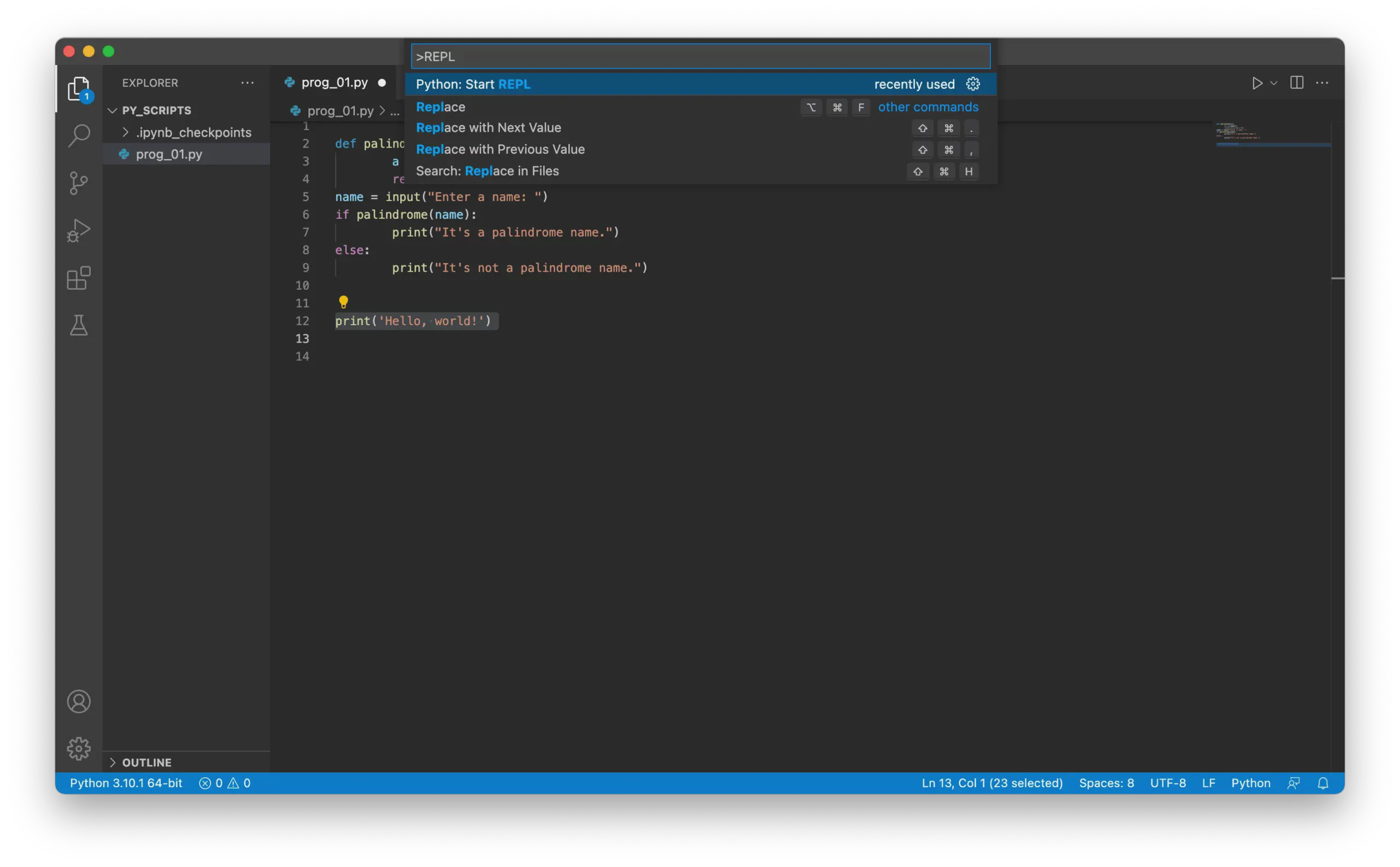
Open the Command Palette (
CMD + SHIFT + P).Search for “REPL” and click on Python: Start REPL:
The interactive Python shell will appear. You can enter commands at the
>>>prompt and see instant results: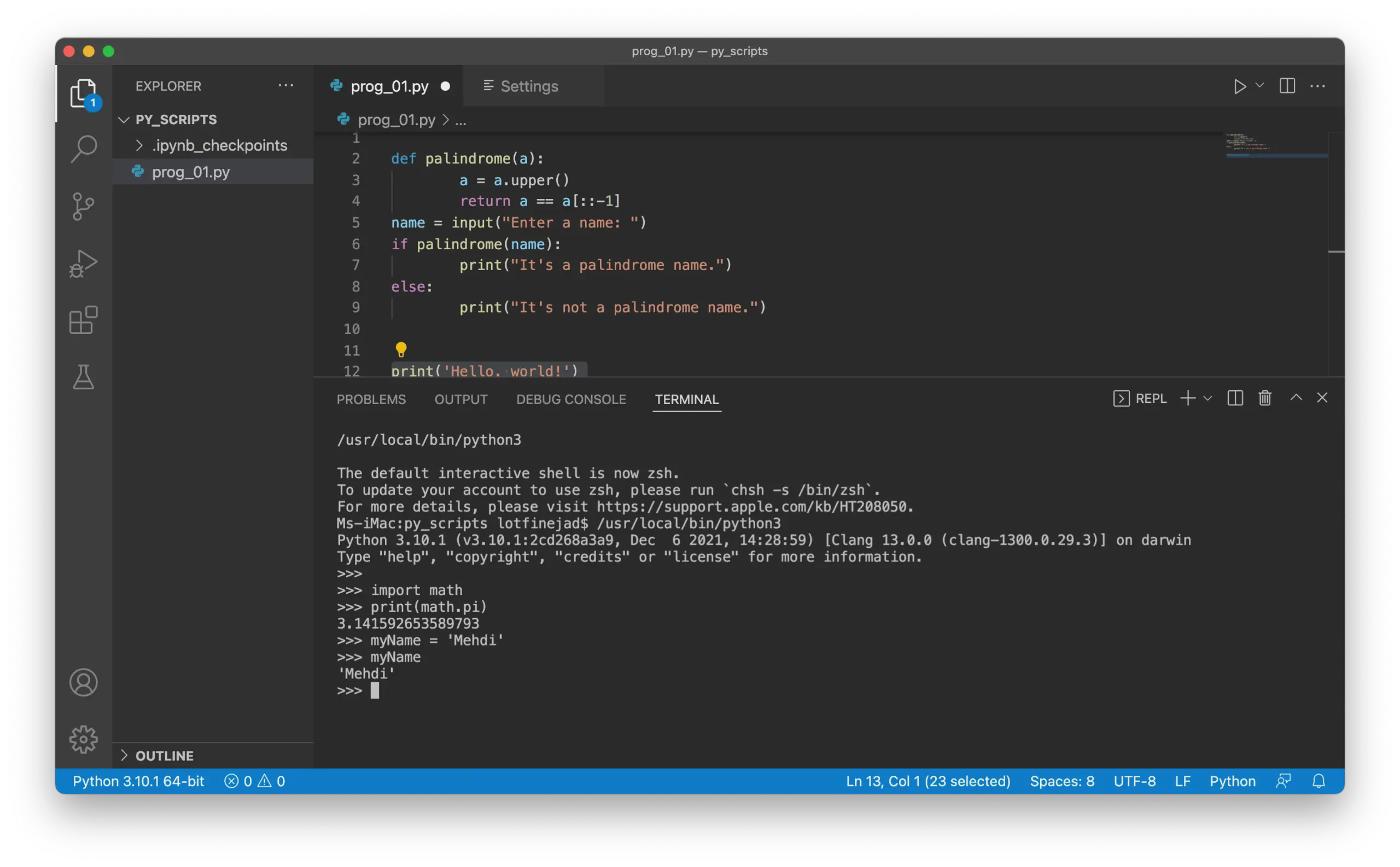
REPL is great for testing small pieces of code or experimenting with APIs.
Formatting Python Code
When writing Python programs, it’s important to follow proper formatting guidelines. Python has a well-known style guide called PEP 8, which makes your code easier to read and understand.
Automatic Formatting with autopep8
To automatically format your code in VS Code, use the autopep8 package.
Install autopep8 Open the integrated terminal and execute the following command:
pip3 install autopep8Configure autopep8 in VS Code
Open the settings in VS Code.
Search for Python formatting.
Set both Autopep8 Path and Provider to
autopep8: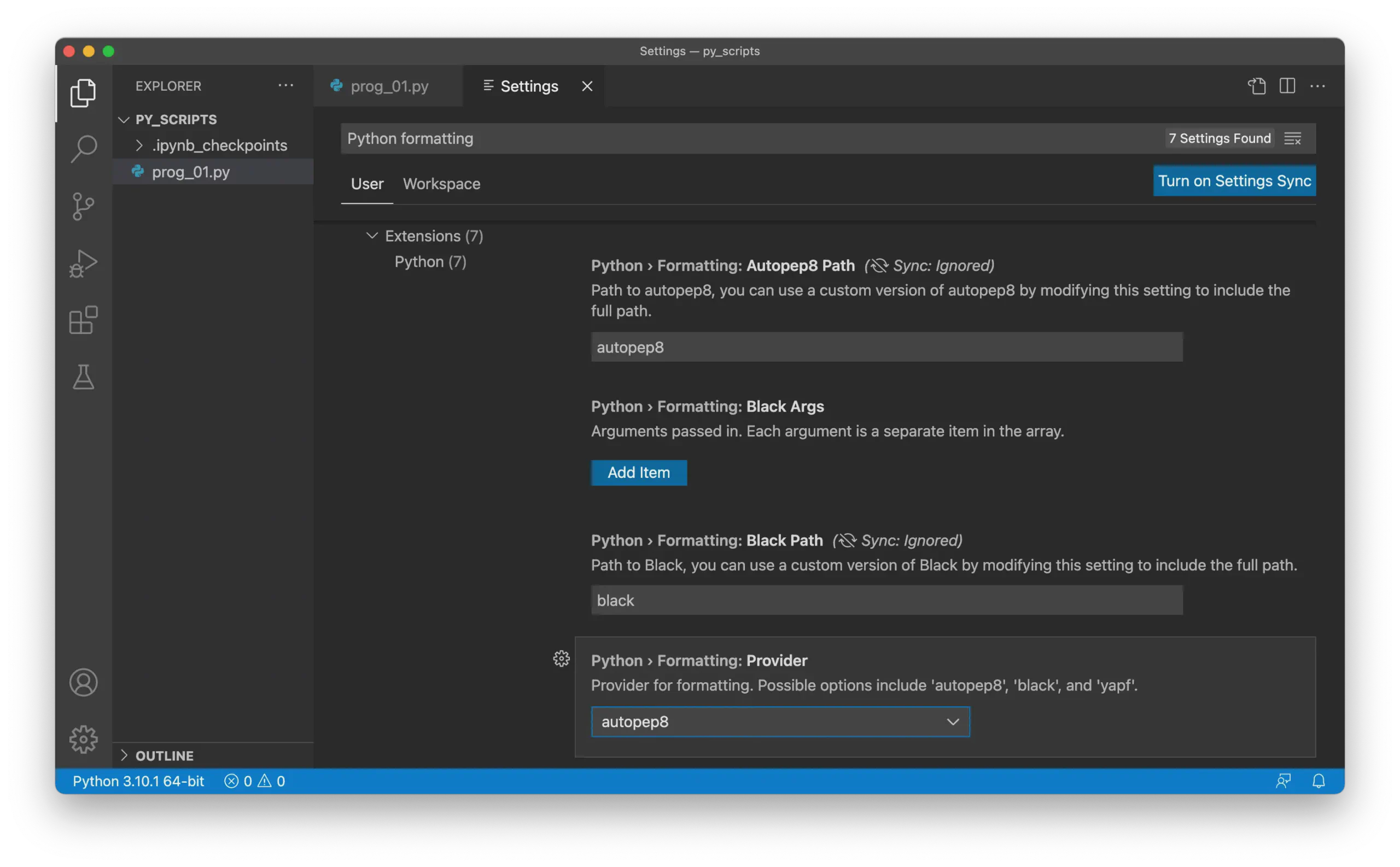
Enable Format on Save
Search for Format On Save in the settings.
Check the Format On Save option:
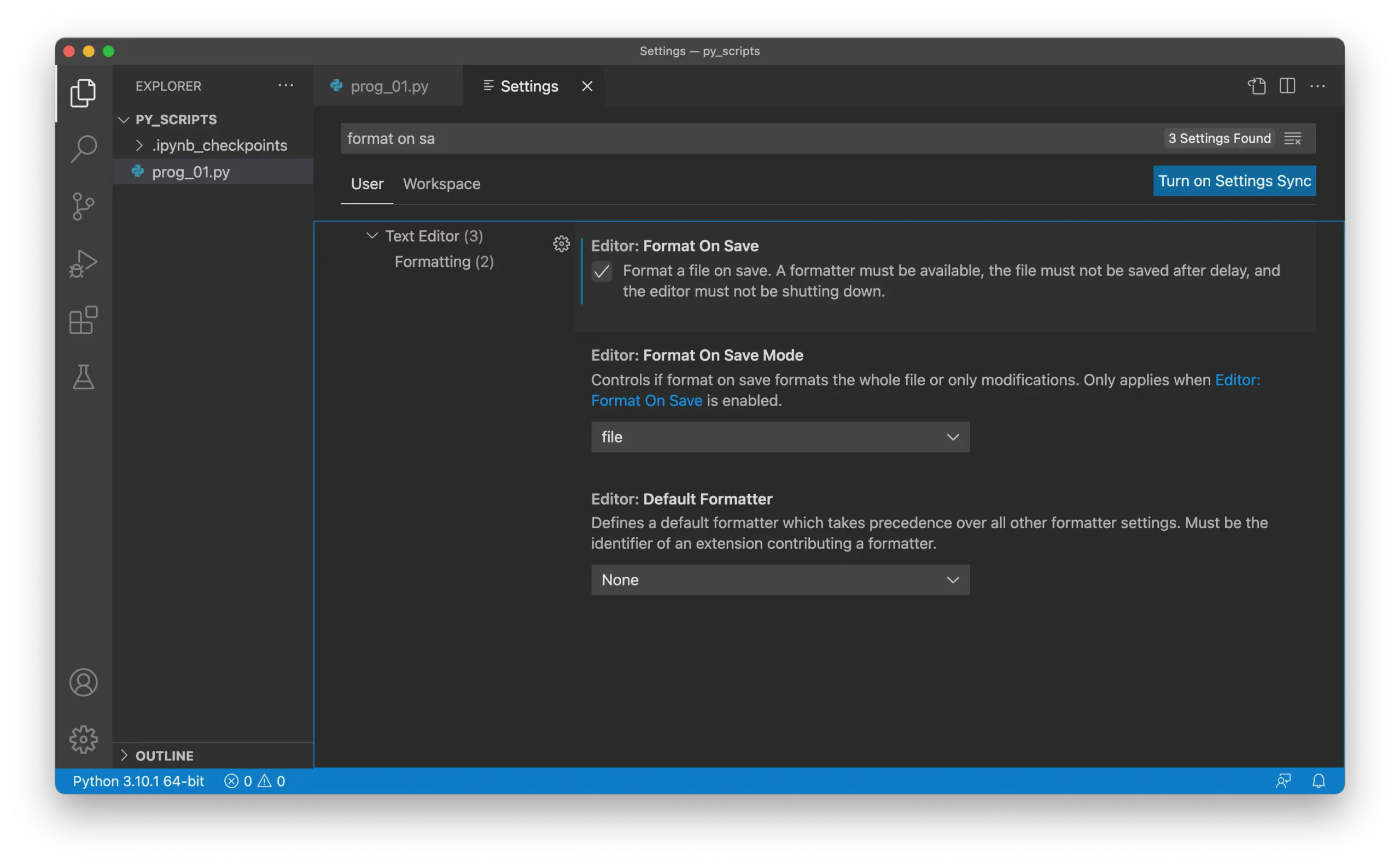
Enabling this option applies all PEP 8 rules automatically whenever you save a Python file.
Refactoring Python Code
What is Refactoring?
Refactoring is the process of restructuring code without changing its external behavior to improve readability and maintainability.
VS Code provides basic refactoring tools through the Python extension, including:
- Rename Symbol
- Extract Method
- Extract Variable
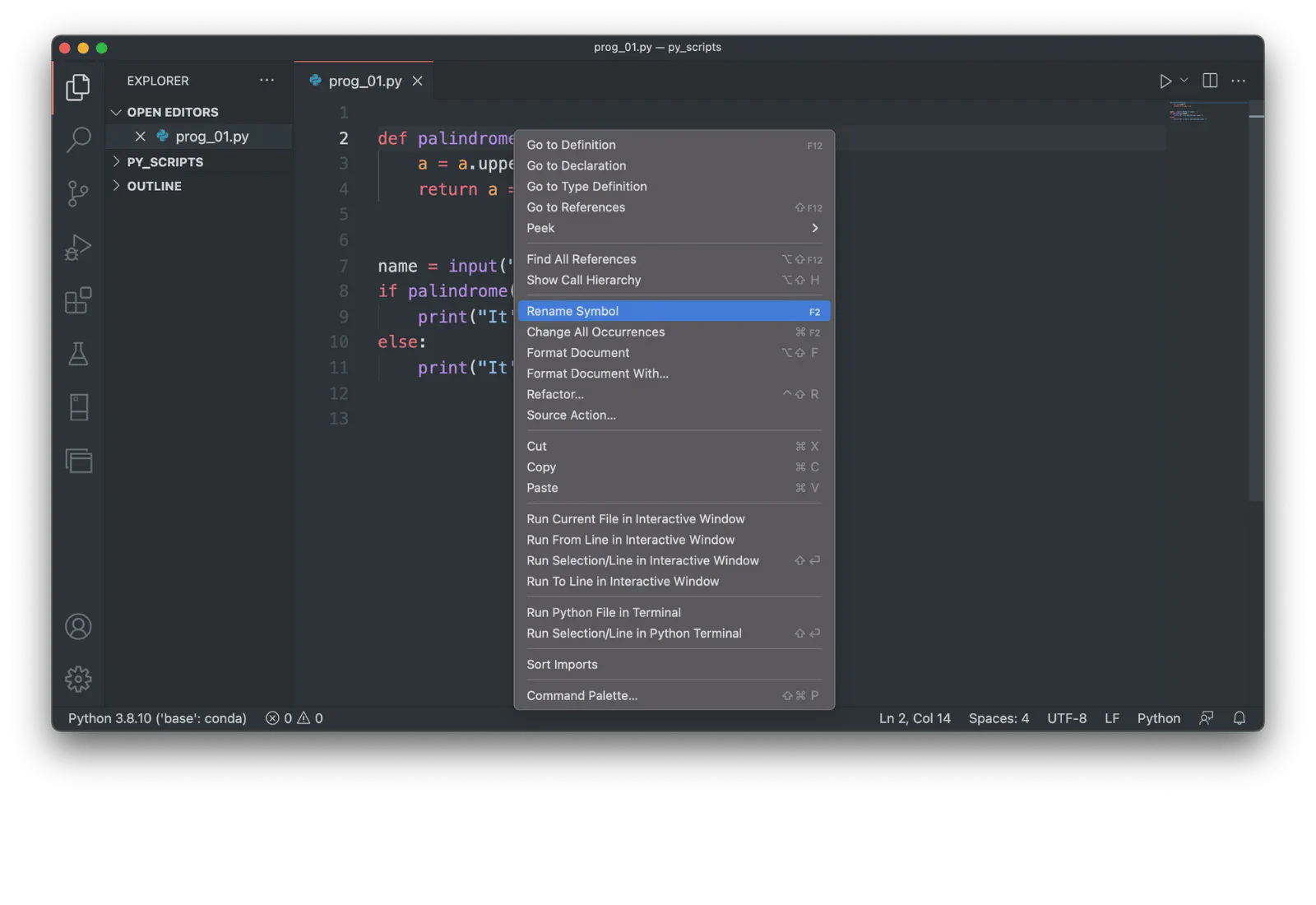
Example: Rename Symbol
To rename a function, right-click on its name and choose Rename Symbol. For example:
Rename
palindrome()tocheck_palindrome().Enter the new name in the text box and press Enter:
All occurrences of
palindromewill be replaced withcheck_palindrome: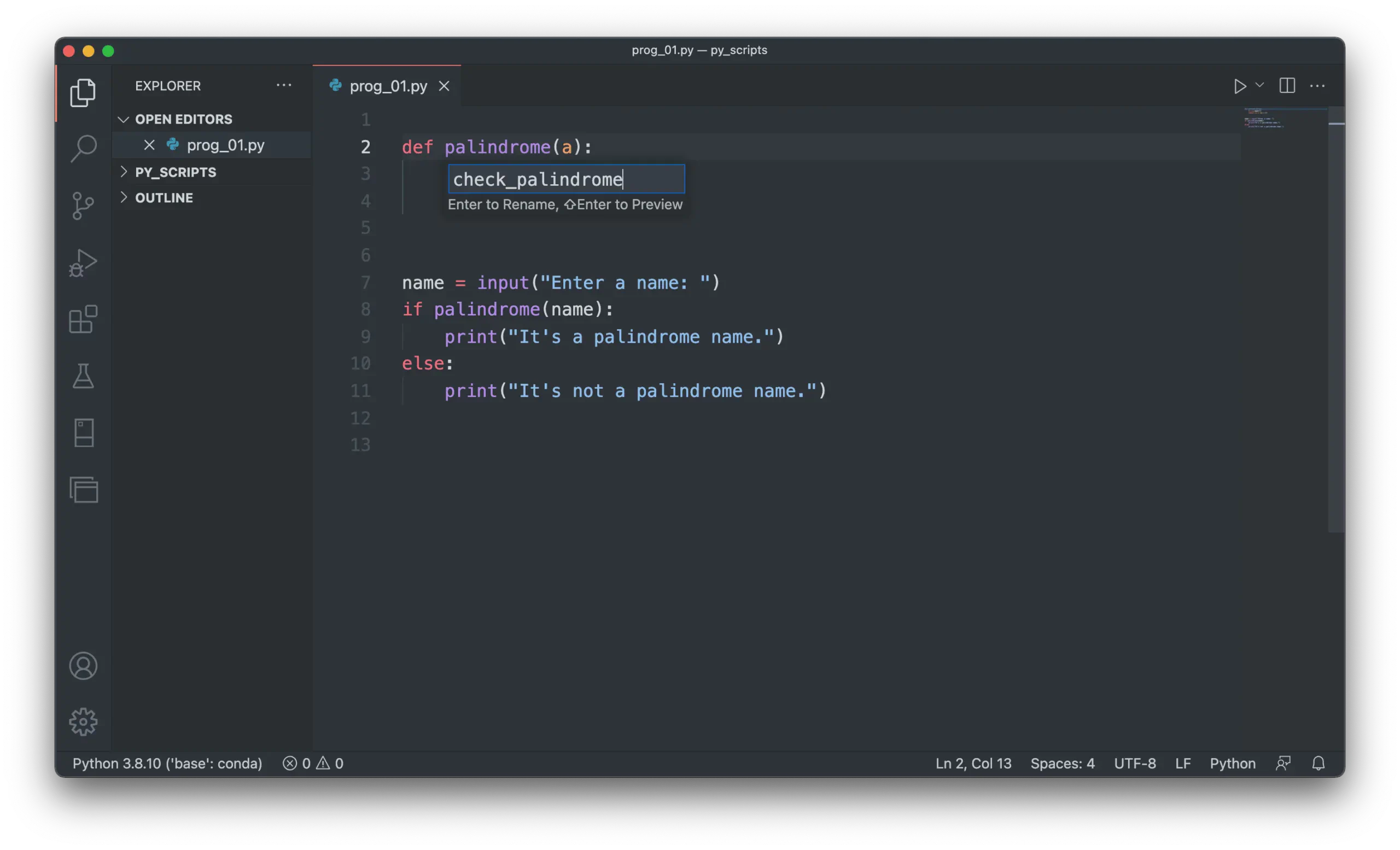
Example: Extract Method
Create a Python file with the following code:
height = 5 width = 4 area = height * width print("Room's area =", area, "square meters")Select the third line, right-click, and choose Refactor from the context menu:
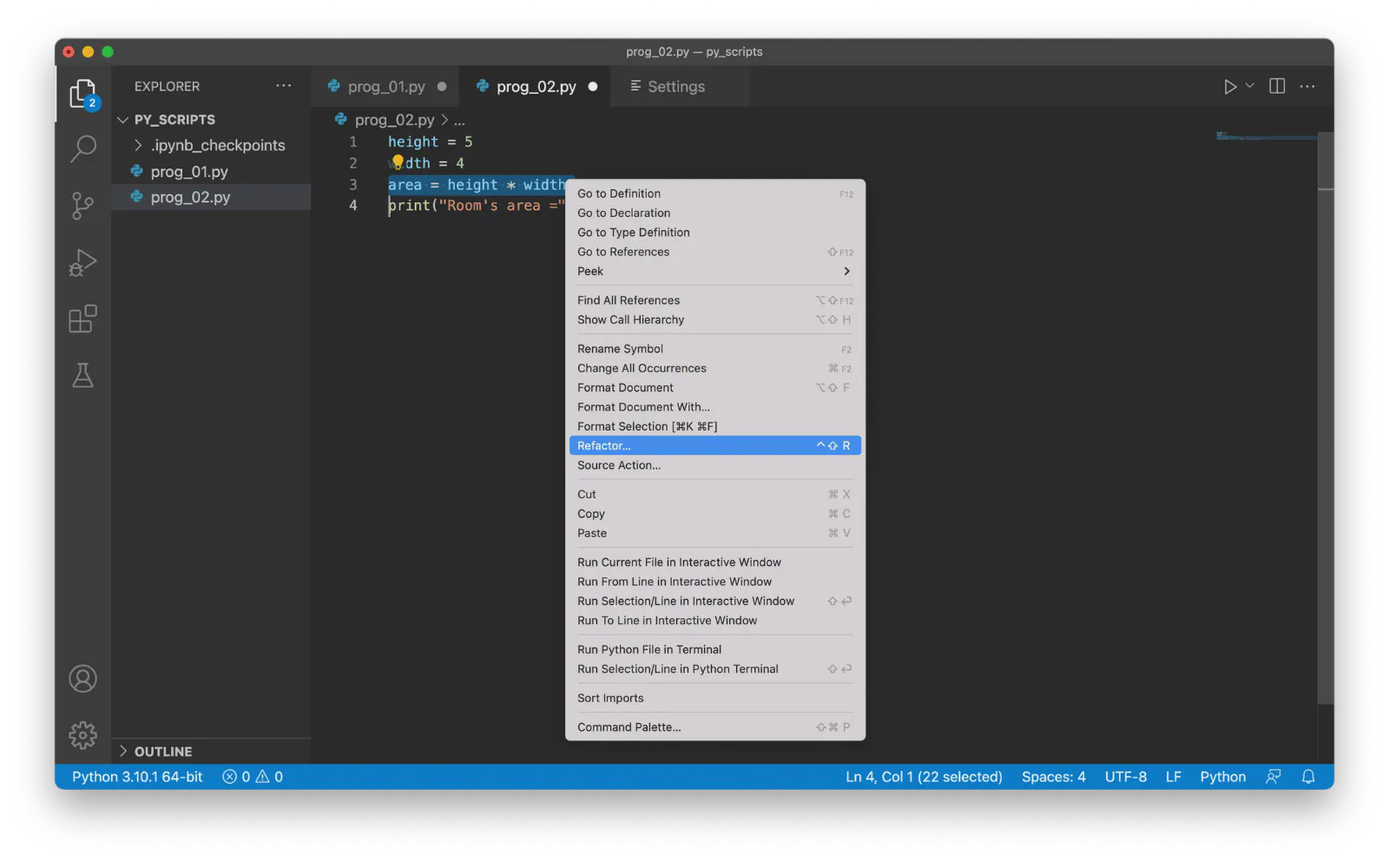
Click Extract Method and enter the new name (e.g.,
calc_area):
Python Interactive Window
VS Code supports working with Jupyter Notebooks.
Right-click on a Python file and select Run Current File in Interactive Window:
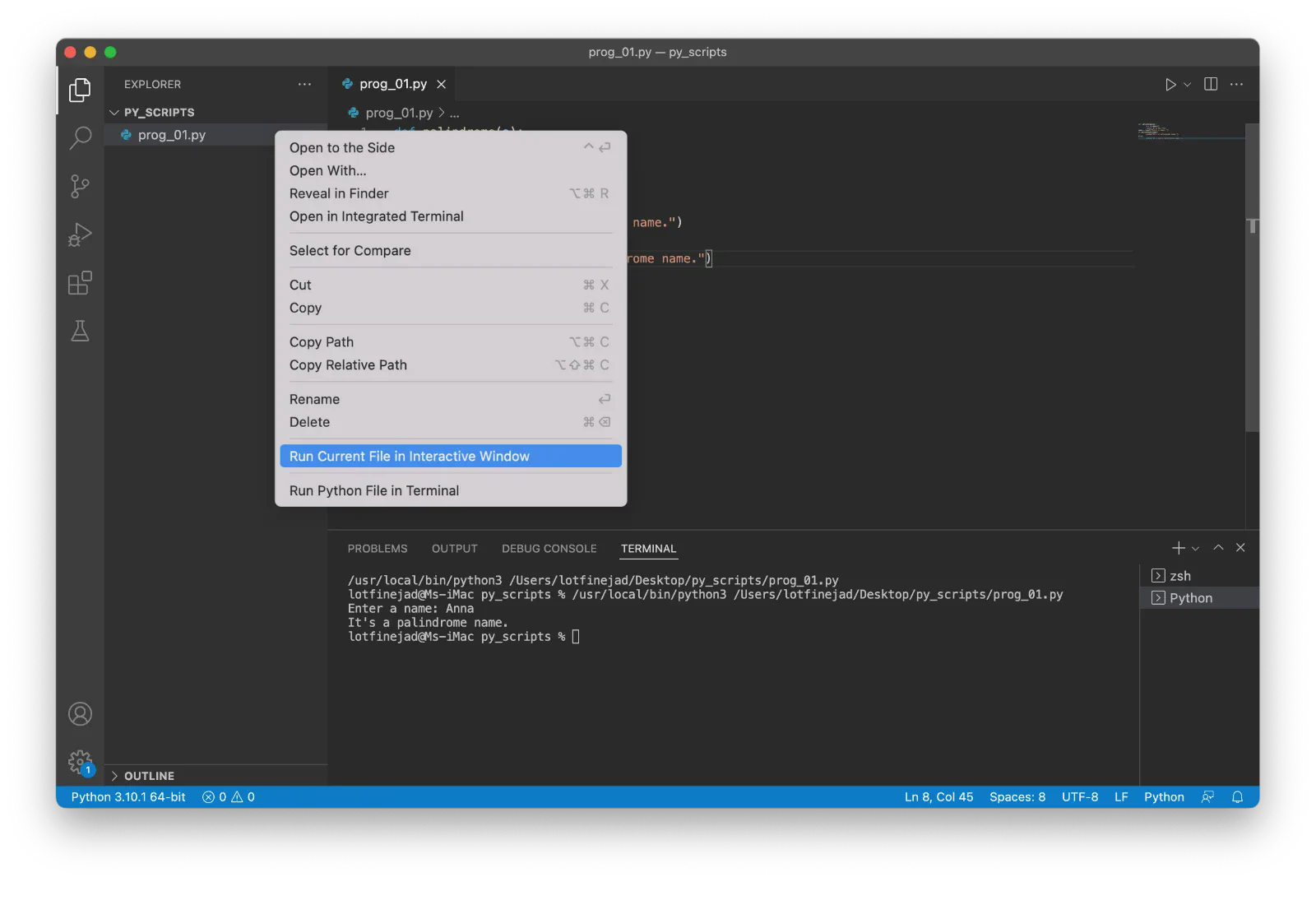
If the Jupyter package isn’t installed, a dialog box will prompt you to install it:
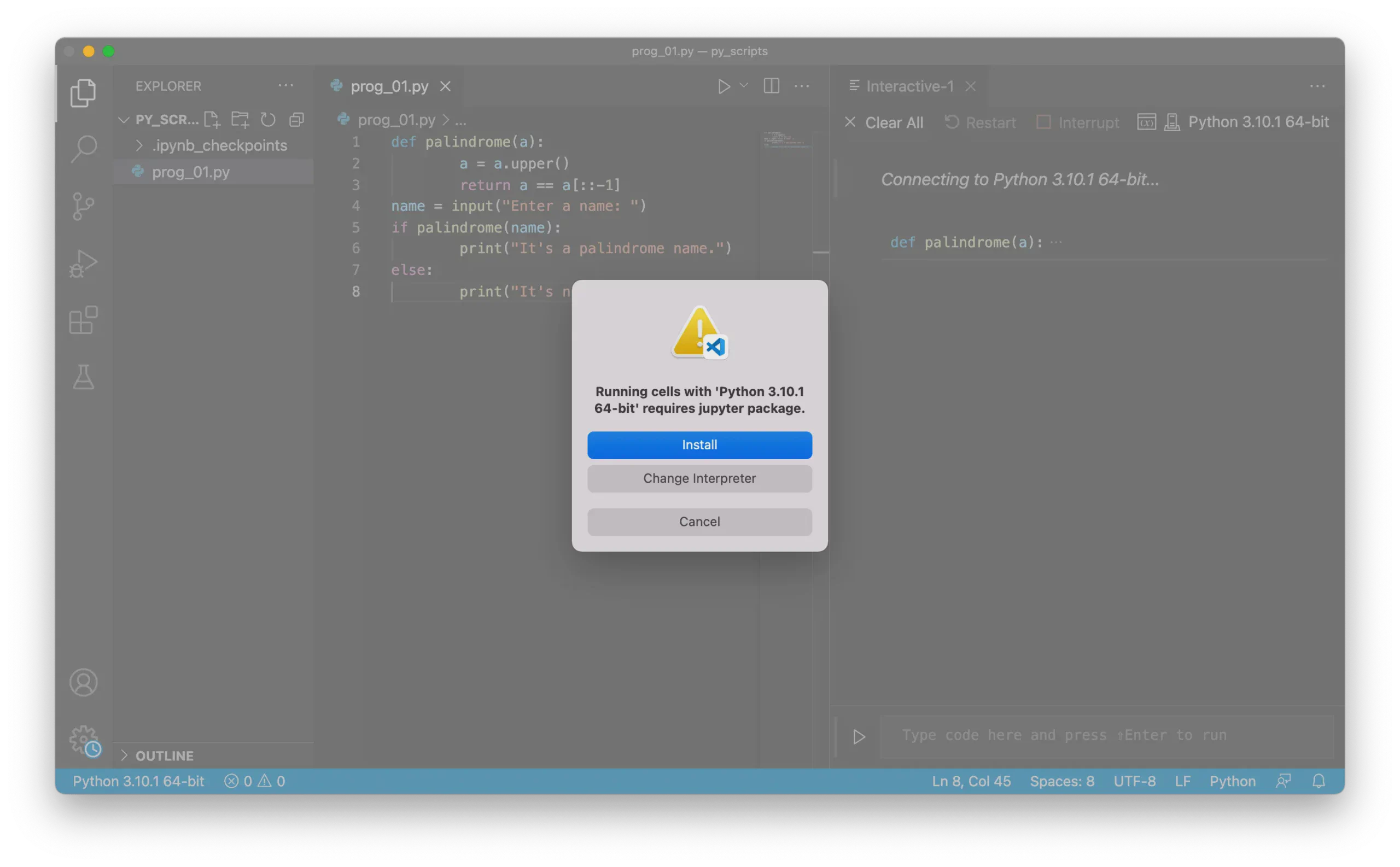
Once installed, an interactive window will appear, allowing you to run the file interactively.
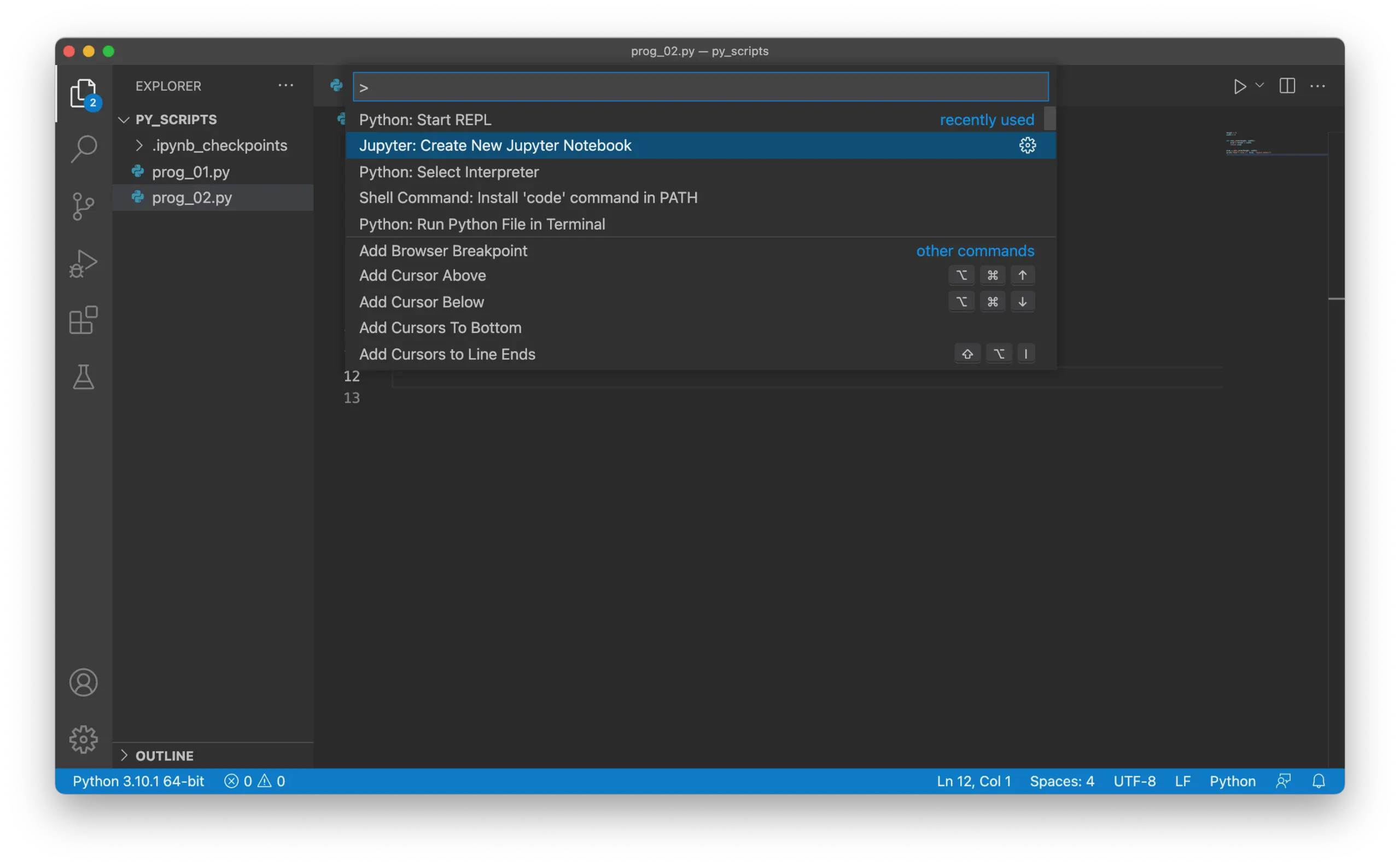
You can also create new Jupyter Notebooks in VS Code:
Open the Command Palette.
Select Jupyter: Create New Jupyter Notebook:
Conclusion
This tutorial covered installing and configuring VS Code, running Python files, and using additional features like REPL, formatting, refactoring, and Jupyter integration.
While we’ve covered a lot, there’s even more to explore in VS Code to enhance your productivity. Dive deeper into its documentation to make the most out of this powerful editor!